SAML app integrations
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based protocol. It's used for Single Sign-On (SSO), and for exchanging authentication and authorization data between apps. Within the SAML workflow, Okta can act as both the identity provider (IdP) or as the service provider (SP), depending on your use case.
SAML is the protocol that most organizations use for SSO and enterprise security. The primary appeal of SAML is that SAML helps reduce the attack surface for organizations and improves the customer's sign-in experience.
When a user signs in to an app using SAML, the IdP sends a SAML assertion to their browser that's passed to the SP. In many circumstances, the IdP verifies the user (with Multifactor Authentication (MFA), for example) before issuing the SAML assertion.
The SAML assertion is an XML file with three statement types: authentication, attribution, and authorization. The authentication statement covers when and how the subject is authenticated. The attribution statement provides details about the user, such as group membership or their role within a hierarchy. Finally, the authorization statement tells the SP which level of authorization the user has across different resources. This way, SAML goes beyond mere authentication and authorizes the user for multiple privileges, protecting your app in the process.
Admins can browse the OIN catalog and set the filter to search for app integrations with SAML as a functionality. When added to an org and assigned to an end user by an admin, the SAML-enabled app integration appears as a new icon on the End-User Dashboard.
Okta as the identity provider
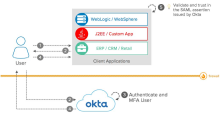
Okta can integrate with SAML 2.0 apps as an IdP that provides SSO to external apps. Okta also supports MFA prompts to improve your app security.
When users request access to an external app registered with Okta, they're redirected to Okta. As the IdP, Okta then delivers a SAML assertion to the browser. The browser uses the assertion to authenticate the user to the SP.
- The user attempts to access apps protected by Okta using SAML for SSO.
- Client apps act as SAML service providers and delegate the user authentication to Okta. The client apps send a SAML assertion to Okta to establish the user session.
- Okta acts as the SAML IdP and uses SSO and MFA to authenticate the user.
- Okta returns an assertion to the client apps through the end user's browser.
- The client apps validate the returned assertion and allow the user access to the client app.
Okta as the service provider
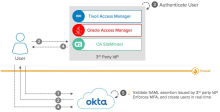
Okta can also serve as the SP that consumes authentication from other SSO solutions like IBM Tivoli Access Manager, Oracle Access Manager, or CA SiteMinder.
In this scenario, if a user tries to sign in to Okta, they're redirected to an external IdP for authentication. After the user has successfully authenticated, the external IdP returns the SAML assertion, which is then passed through the user's browser to access the Okta services.
- The user opens Okta in a browser to sign in to their cloud or on-premises app integrations.
- Okta acts as the SP and delegates the user authentication to the external IdP.
- The external IdP authenticates the user.
- The IdP sends a SAML assertion back to Okta.
- Okta validates the SAML assertion from the external IdP and, if necessary, enforces MFA. Users can be created in Okta using Just-In-Time provisioning if required.
Users, client apps, and external IdPs can all be on your intranet and behind a firewall, provided that the end user can reach Okta through the internet.
Related topics
Understanding SAML - Okta Developer