Client certificate validation behavior
Certificate validation behavior is an Early Access feature. To enable it, contact Okta Support.
Topics
Background
Access Gateway makes use of certificates in various ways:
- To establish and manage SSL/TLS. See Certificate use.
- As an additional authentication method when validating requests.
In the second scenario, a certificate chain is loaded into Access Gateway and requests containing a client certificate are validated against valid end user certificates from that chain.
In general, certificate chains are composed of:
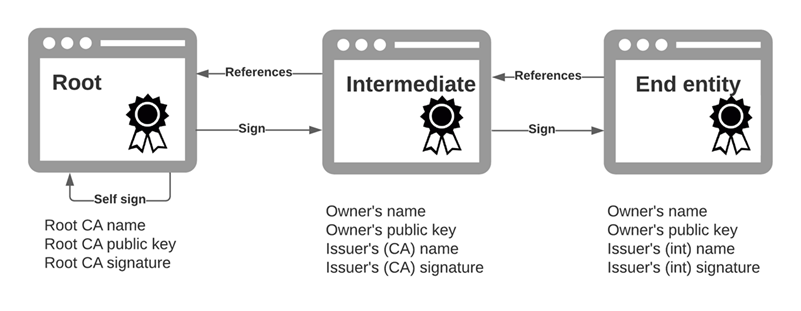
- A root certificate, provided by a known certificate authority such as DigiCert, Thawte or a similar provider.
- one or more Intermediate certificates, typically assigned to a company and signed by a root CA. There can and often are multiple intermediate certificates. For example by department or division within a given company.
- End entity certificates, the final certificate assigned to a given entity. End entity certificates are used for validation.
Access Gateway and certificate chains
Access Gateway uses certificate chains to validate applications using behaviors. The aspects of the process are:
- Manage certificate chains - The Access Gateway Management console is used to add, view, and otherwise manage certificate chains.
- Update certificate revocation lists- Access Gateway periodically refreshes Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) using the lifetime and refresh intervals specified in the management console. See Manage CRL settings in Certificate chain operations.
- Specify certificate validation - Applications validate against certificates using the valid certificate behavior. See Certificate validation behavior in Define app behaviors
At run-time, when enabled, application requests are validated against one of the certificate validation behaviors, including:
- Default behavior, no certificate based validation occurs.
- On certificate validation failure:
- Forward the request to a custom URL/URI.
- Display a blank page but return a 405 status code.
- Display an invalid certificate error page.
