Add a portal application
Create and configure a header-based application to route incoming traffic to specific back-end servers.
Access Gateway applications can use policies and specialized policy configurations to create portal applications. A portal directs some traffic to specific back-end servers based on access policy and URI requests, and directs any remaining traffic to another back-end server.
Architecture
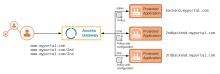
When a user requests a resource, the portal receives the request and routes it to an appropriate back-end server. Each request consists of a core URL (www.myportal.com) and specific resources, which are the elements that follow the core URL (/2nd in the architecture diagram).
In the architecture diagram, requests to www.myportal.com/2nd are routed to 2ndbackend.myportal.com. Similarly, requests to www.myportal.com/3rd are routed to 3rdbackend.myportal.com. Other requests are routed to backend.myportal.com.
Rewrites
Portal applications use custom policies and configurations to define access to multiple back-end servers. A default policy redirects URIs that don't fall under other policies to a default back-end application. Additional policy statements and their configurations are used to rewrite requests and redirect the requests to specific back-end applications.
This table provides examples of how user requests are rewritten to meet the expected behaviors:
| User request | Expected behavior |
Inbound and outbound rewrites |
|---|---|---|
| myportal.com/ | Redirect to backend.myportal.com. | backend.myportal.com
myportal.com/ |
| myportal.com/abc.htm | Redirect to backend.myportal.com/abc.htm. | backend.myportal.com/abc.htm
myportal.com/abc.htm |
| myportal.com/2nd | Redirect to 2ndbackend.myportal.com based on /2nd. | 2ndbackend.myportal.com
myportal.com/2nd |
| myportal.com/2nd/efg.html | Redirect to 2ndbackend.myportal.com based on /2nd.
Strip /2nd from the string for inbound rewrites. Add /2nd back to the string for outbound rewrites. |
2ndbackend.myportal.com/efg.htm
myportal.com/2nd/efg.htm |
| myportal.com/3rd | Redirect to 3rdbackend.myportal.com based on /3rd. | 3rdbackend.myportal.com
myportal.com/3rd |
| myportal.com/3rd/hij.html | Redirect to 3rdbackend.myportal.com based on /3rd.
Strip /3rd from the string for inbound rewrites. Add /3rd back to the string for outbound rewrites. |
3rdbackend.myportal.com/hij.htm
myportal.com/3rd/hij.htm |
Policies
Default
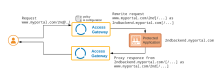
The default policy is applied to all requests that don't match some other specific policy. The default policy causes requests to be rewritten against the default application domain and then forwarded to the back-end application. After the request is serviced the result is rewritten back to the original domain and returned.
Rewrite policy for requests to /2nd
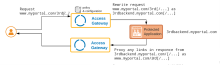
Each subsequent back-end includes a policy and advanced configuration to rewrite requests as required. In this example, the policy specifies /2nd as the root URI that triggers a rewrite. The rewriting rules remove the URI and redirect the request to a secondary back-end application (2ndbackend.myportal.com).
Rewrite policy for requests to /3rd
Each subsequent back-end includes a policy and advanced configuration to rewrite requests as required. In this example, the policy specifies /3rd as the root URI that triggers a rewrite. The rewriting rules remove the URI and redirect the request to a secondary back-end application (3rdbackend.myportal.com).
Before you begin
- Determine the external URL used by the application, in this example www.myportal.com.
- Determine the possible URI and back-end combinations. The sample architecture uses the following combinations:
- www.myportal.com/2nd > 2ndbackend.myportal.com.
- www.myportal.com/3rd > 3rdbackend.myportal.com.
All other URIs use backend.myportal.com as their back-end.
- Determine all required header attributes required for authentication.
Typical workflow
|
Task |
Description |
|---|---|
| Create a containing group |
Create an optional group to be assigned to the application. |
| Create header application |
Create a header application that defaults to the shared common back-end. |
| Assign a certificate to a portal application |
Assign an optional certificate to the application. |
| Add additional attributes |
Add optional, but often necessary, additional attributes to the application. |
| Add required access policy |
Add all required policies for all serviced URIs. |
| Test the application |
Test the application using header and policy simulation. |