Single cluster CIAM application reference architecture
The single cluster Access Gateway is an architecture representing the components required for protecting a single web resources using Access Gateway. It extends the simple Access Gateway instance architecture by introducing an Access Gateway cluster.
This architecture is designed to meet the following requirements:
- Secure access to a single application - Accessible to the external internet.
- Provide fault tolerance - Providing additional instances of Access Gateway, as cluster workers, such that if one is unavailable the cluster continues to perform normally.
- Manage capacity - Providing additional instances of Access Gateway to handle expected load.
Benefits and drawbacks
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Architecture
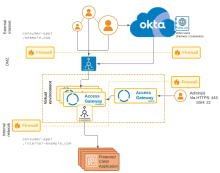
Components
| Location | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| External internet | Web client |
Traditional client browser accessing Access Gateway using known as [appN|consumer-app1].example.com URLs. |
| Okta org |
Your Okta org, providing identity services. |
|
| Okta org Universal Directory |
Okta Universal Directory, housed in an Okta org, containing users outside other LDAP or Active Directory implementations. Typically these include other customer accounts, partner accounts, and more. |
|
| Firewall | External internet to DMZ | Traditional firewall between the external internet and the DMZ hosting Access Gateway. |
| Internal network | ||
| Access Gateway admin | Access Gateway admin node, in any of the data centers handling configuration, configuration backups, log forwarding and similar activities. Access by administrators within the internal network. |
|
| Pre Access Gateway load balancer |
Balances load between clients and the Access Gateway cluster. Positioned between clients and the Access Gateway cluster. |
|
| Access Gateway | Access Gateway instance, located in the DMZ is used to provide access to applications used by external internet clients. Typically hosted in a virtual environment such as Amazon Web Services, MS Azure, Oracle OCI or something similar. See Manage Access Gateway deployment. |
|
| Internal application load balancer | Balances load between the Access Gateway cluster and the protected applications. See Load balancing. | |
| comsumer-app1.example.com |
URL representing one of the applications a web client would enter to access one of the applications secured by Access Gateway. Typically all URLs of this nature are served by, and resolve to, the Access Gateway instance. |
|
| Protected application | The set of protected web resources, accessed using the consumer-app1.internal-example.com URLs. The traditional or historic application Access Gateway interacts with using the Protected Web Resource field within each application definition. |
Other considerations
DNS is typically split between external and internal domains. All external URLs, such as [appN|consumer-app1].example.com, would be served externally and point to the Access Gateway instance. Internal URLs, used by Access Gateway such as [protd-N|consumer-app1].internal-example.com, would be served by internal DNS.
Most architectures forward log events to an external syslog component. Okta strongly recommends that a logging server be configured for all Access Gateway environments. See Configure log forwarders.
Not shown in this architecture are the data centers housing architecture components.
