Kerberos simple cluster application reference architecture
The simple Kerberos cluster Access Gateway architecture represents a set of components required for Kerberos based authentication and authorization using Access Gateway. It extends the single Kerberos instance by adding an Access Gateway cluster.
This architecture is designed to meet the following requirements:
- Protect a Kerberos (Windows IIS) based service.
- Meet basic fault tolerance and high availability needs for Access Gateway.
Benefits and drawbacks
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Architecture
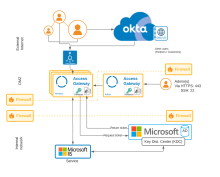
Components
|
Location |
Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| External internet | Web clients |
Traditional client browser accessing Access Gateway using known as [appN|consumer-app1].example.com URLs. |
| consumer-app1.example.com
URLs not shown |
URL representing the application an external web client would enter to access one of the applications secured by Access Gateway. Typically all URLs of this nature are served by, and resolve to, the Access Gateway instance. |
|
| Okta org |
Your Okta org, providing identity services. |
|
| Okta org Universal Directory |
Okta Universal Directory, housed in an Okta org, containing users outside other LDAP or Active Directory implementations. Typically these include other customer accounts, partner accounts, and more. |
|
| Firewall |
External internet to DMZ |
Traditional firewall between the external internet and the DMZ hosting Access Gateway. |
| DMZ | Load balancer | Pre load balancer balances load between clients and the cluster. Positioned between clients and the cluster. |
| Access Gateway | Access Gateway cluster, located in the DMZ is used to provide access to applications used by external internet clients. Contains a Kerberos service and a keytab. Typically hosted in a virtual environment such as Amazon Web Services, MS Azure, Oracle OCI, or similar. See Manage Access Gateway deployment. See Create keytab for details of creating a keytab. See Add Kerberos service for details of defining a Access Gateway Kerberos service. |
|
| Firewall |
DMZ to internal firewall |
Traditional firewall between DMZ and the internal network. |
| Internal network | Service/Protected application |
The set of protected web resources, in this case Microsoft Services, accessed using the comsumer-app1.internal-example.com URLs.
Supported versions:
|
| Pre internal Kerberos domain load balance | Load balancer for the Kerberos domain service cluster | |
| Microsoft domain service cluster with Key Distribution Center |
Domain service cluster containing a Key Distribution Center (KDC). In this architecture, the Domain service/KDC represents multiple instances acting as a cluster. |
Other considerations
DNS is typically split between external and internal domains. All external URLs, such as [appN|consumer-app1].example.com, would be served externally and point to the Access Gateway instance. Internal URLs, used by Access Gateway such as [protd-N|consumer-app1].internal-example.com, would be served by internal DNS.
Most architectures forward log events to an external syslog component. Okta strongly recommends that a logging server be configured for all Access Gateway environments. See Configure log forwarders.
Additionally, Access Gateway itself is typically managed via internal access only. That is, administrators typically access Access Gateway itself from behind the firewall. This is shown in other architectures.
