Masked DNS protected application reference architecture
The Masked DNS protected application Access Gateway architecture is the first step in isolating a protected web resource from the external internal.
In this architecture the protected web resource internal URL and the external URL are served by different DNS, effectively hiding or masking the actually application URL. In addition, the internal DNS server is isolated from the external web. Application users, in both the internal and external cases, use the same URL, which is directed to Access Gateway. The protected web application is then 'masked' in that only Access Gateway accesses the protected web application by its internal, or 'masked' DNS name.
Benefits and drawbacks
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Architecture
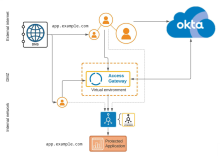
Note that while hidden or masked, the protected web resource is still accessible by name or IP, from both the internal and external networks, if the masked DNS name or IP address is known.
Components
|
Location |
Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| External internet | External URL | External URL used by clients to access Access Gateway on behalf of the protected web resource. |
| DNS | DNS server providing DNS resolution for external URL. | |
| DMZ | Access Gateway | Access Gateway cluster, located in the DMZ, uses multiple DNS servers to resolve internal and external URLs. |
| Internal network |
Internal DNS and URL |
Internal DNS server serving internal URL representing protected web resource in Access Gateway. |
|
Load Balancer |
Internal load balancer. In some situations it may be possible to substitute Access Gateway as a load balancer. |
|
| Application | Protected web resource (application) |
