Firewall protected application reference architecture
The Firewall protected application Access Gateway architecture extends the Masked DNS architecture to add firewalls between the external internal/DMZ and DMZ/internal network. In this architecture the application, the protected web resource internal URL and the external URL are served by different DNS with internal DNS server isolated the external DNS. This architecture meets the following requirements:
- Protects the protected web resource by hiding the internal URL from external clients.
- Firewalls protected unauthorized requests.
Benefits and drawbacks
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Architecture
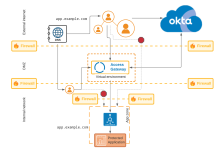
In the firewall architecture, external access to the protected web application is defined by the external network/DMZ firewall. Additionally, internal access to the application is denied by the internal/app zone firewall. This architecture effectively shields all unauthorized access to the protected web resource.
Components
|
Location |
Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| External internet | External URL | External URL used by clients to access Access Gateway on behalf of the protected web resource. |
| DNS | DNS server providing DNS resolution for external URL. | |
| Between external internet and DMZ | Firewall | Firewall separating DMZ housing Access Gateway and the external internet. |
| DMZ | Access Gateway | Access Gateway cluster, located in the DMZ, uses multiple DNS servers to resolve internal and external URLs. |
| Between internal internet and DMZ | Firewall | Firewall separating DMZ housing Access Gateway and the internal internet. |
| Internal network | App zone | A internal network zone where the protected web resource is housed. |
| App zone firewall | An internal firewall separating the app zone from the rest of the internal network. | |
| Internal DNS and URL | Internal DNS server serving internal URL representing protected web resource in Access Gateway. | |
| Application | Protected web resource (application) |
