Unprotected application reference architecture
The unprotected application architecture is a baseline or starting point after an application is integrated with Access Gateway. It's the state before any configuration to deny direct access to the back-end protected web resource has been made. In this architecture, a single application, referred to as a protected web resource, is served to requesting clients using Access Gateway. All URLs (Access Gateway and the back-end protected web resource) are typically resolvable using a single DNS server and are accessible to all. This architecture meets the following requirements:
- No specialized configuration is required.
- URLs (Access Gateway and application) are entered into DNS but no further action is taken.
- It can be used as a baseline for testing and development.
Benefits and drawbacks
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
Architecture
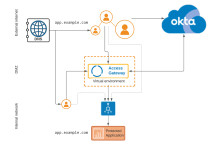
In this architecture, external clients can access the application directly if they know the internal URL/IP. Likewise internal network clients can also access the application directly. Represented by neither dotted access path being blocked.
Components
|
Location |
Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| External internet | External URL | External URL used by clients to access Access Gateway on behalf of the protected web resource. |
|
DNS |
DNS server providing DNS resolution for both the external URL and the internal (protected web resource |
|
| DMZ | Access Gateway | The Access Gateway cluster provides access to applications used by external internet clients. It's housed in the DMZ. It's typically hosted in a virtual environment such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Oracle OCI, or similar. See Manage Access Gateway deployment. |
| Internal network |
Internal URL |
The Internal URL, represented by the protected web resource in Access Gateway. |
| Application | The protected web resource, also referred to as the application. | |
